XSCOPE File I/O#
This FreeRTOS example application reads a WAV file from the host over an XSCOPE server, propagates the data through multiple threads across both tiles, and then writes the output to a WAV file on the host PC, also over an XSCOPE server.
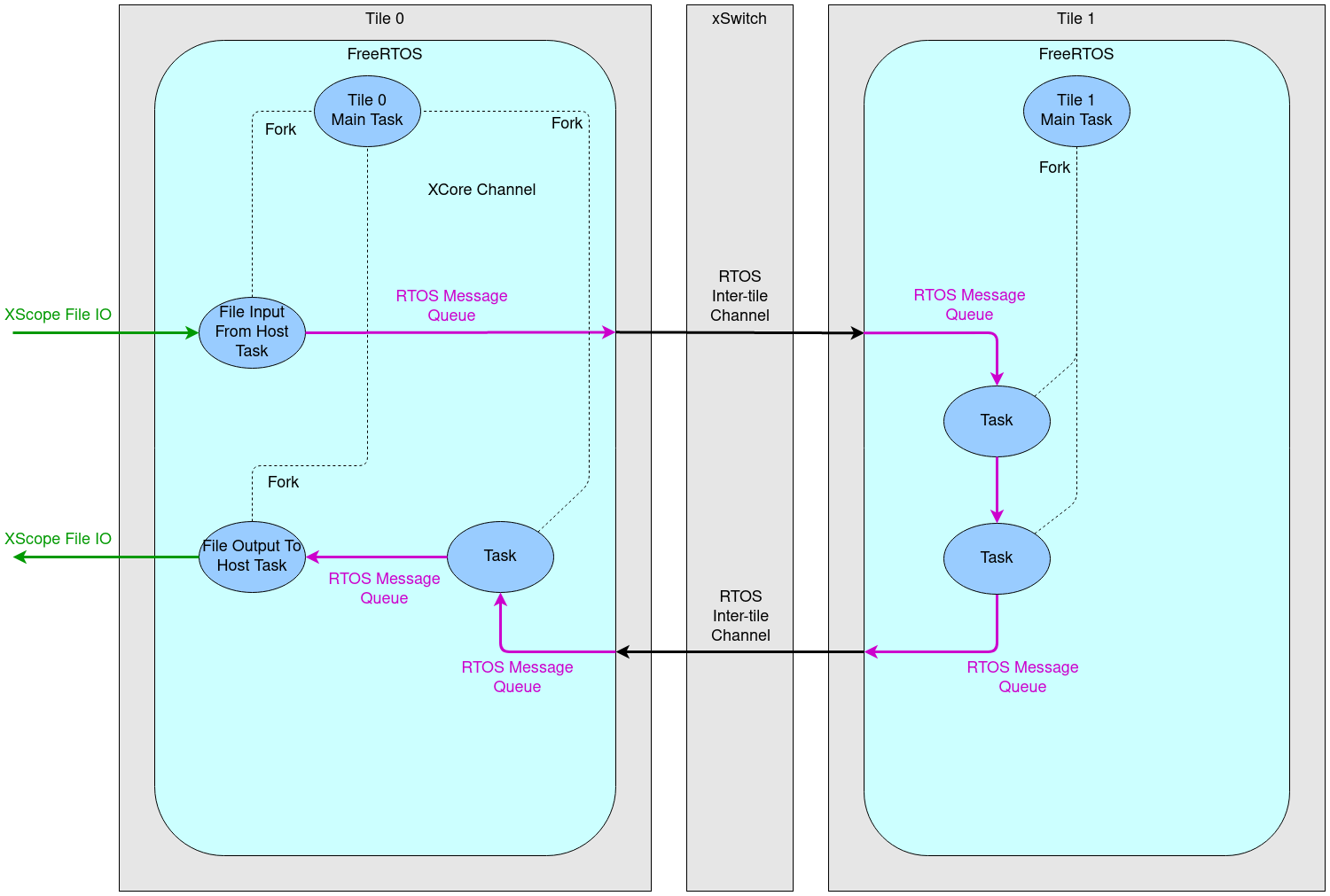
The 3-stage pipeline in the example covers both XCORE tiles. Stage #1 and Stage #2 run on tile[1], while Stage #3 runs on tile[0].
Stages #1 and #2 are implemented in the functions stage_1 and stage_2 which can be found in the file src\data_pipeline\src\data_pipeline_tile1.c. In this example, both stages apply a fixed gain to the PCM audio samples. In stage_1, preemption is disabled with the rtos_interrupt_mask_all() function to insure the FreeRTOS kernel does not interrupt the task and perform a context switch during a performance critical code section. stage_2 is a typical FreeRTOS task which can be preempted. However, this example is rather simple so, instead of leaving a context switch up to chance, the stage_2 function periodically yields to the FreeRTOS kernel - emulating a context switch.
Both the stage_1 and stage_2 functions have been instrumented with a stopwatch-like timer to measure the time spent applying the fixed gain.
Stage #3 is implemented in the function stage_3 which can be found in the file src\data_pipeline\src\data_pipeline_tile0.c. In this example, Stage 3 does nothing. It is provided to demonstrate a multi-tile pipeline.
The example application input file name is hard-coded to in.wav and the output file file name is hard-coded to out.wav. Running the application can be wrapped in a simple script if alternative file names are desired. Simply copy your file to in.wav, run the applications, then copy out.wav to you preferred output file name.
The example input file provided is 16 KHz, however, 48 KHz will also work. The input file sample rate must be 32 bits per sample.
This example is already configured to link with the XMOS vectorized math library. Users wishing to take advantage of the vector processing unit (VPU) on the XMOS XS3 architecture can use this example application as a starting point.
Deploying the firmware with Linux or macOS#
Building the host application#
Run the following commands in the root folder to build the host application using your native x86 Toolchain:
Note
Permissions may be required to install the host applications.
cmake -B build_host
cd build_host
make xscope_host_endpoint
make install
The host application, xscope_host_endpoint, will be installed at /opt/xmos/bin/, and may be moved if desired. You may wish to add this directory to your PATH variable.
Before running the host application, you may need to add the location of xscope_endpoint.so to your LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable. This environment variable will be set if you run the host application in the XTC Tools command-line environment. For more information see Configuring the command-line environment.
Building the firmware#
Run the following commands in the root folder to build the embedded application using the XTC Toolchain:
cmake -B build -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=xmos_cmake_toolchain/xs3a.cmake
cd build
make example_freertos_xscope_fileio
Running the firmware#
From the build folder run:
make run_example_freertos_xscope_fileio
In a second console, run the host xscope server:
./xscope_host_endpoint 12345
Deploying the firmware with Windows#
Building the host application#
Run the following commands in the root folder to build the host application using your native x86 Toolchain:
Note
Permissions may be required to install the host applications.
Before building the host application, you will need to add the path to the XTC Tools to your environment.
set "XMOS_TOOL_PATH=<path-to-xtc-tools>"
Then build the host application:
cmake -G "NMake Makefiles" -B build_host
cd build_host
nmake xscope_host_endpoint
nmake install
The host application, xscope_host_endpoint.exe, will be install at <USERPROFILE>\.xmos\bin, and may be moved if desired. You may wish to add this directory to your PATH variable.
Before running the host application, you may need to add the location of xscope_endpoint.dll to your PATH. This environment variable will be set if you run the host application in the XTC Tools command-line environment. For more information see Configuring the command-line environment.
Building the firmware#
Run the following commands in the root folder to build the embedded application using the XTC Toolchain:
set PATH=%PATH%;<path-to-nmake>
To build the embedded application:
cmake -G "NMake Makefiles" -B build -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=xmos_cmake_toolchain/xs3a.cmake
cd build
nmake example_freertos_xscope_fileio
Running the firmware#
From the build folder run:
nmake run_example_freertos_xscope_fileio
In a second console, run the host xscope server:
xscope_host_endpoint.exe 12345